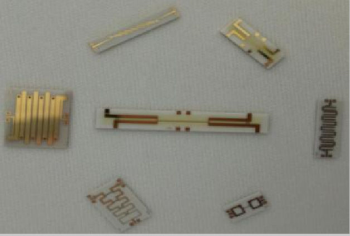
 BMBP28/8-8DA
BMBP28/8-8DA
$49 /Piece
 BMBP22/1-6PA
BMBP22/1-6PA
$49 /Piece
 BMBP39R5/3-6PA
BMBP39R5/3-6PA
$49 /Piece
 BMBP38R6/3R4-6PA
BMBP38R6/3R4-6PA
$49 /Piece
 BMBP38R1/9R9-6PA
BMBP38R1/9R9-6PA
$49 /Piece
 BMBP34R5/3R4-6PA
BMBP34R5/3R4-6PA
$49 /Piece
 BMBP33R5/3R4-6PA
BMBP33R5/3R4-6PA
$49 /Piece
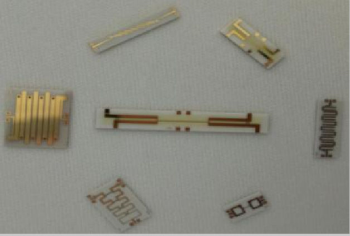 BMBP30R75/1R3-6PA
BMBP30R75/1R3-6PA
$49 /Piece
 BMBP30R7/3R8-6PA
BMBP30R7/3R8-6PA
$49 /Piece
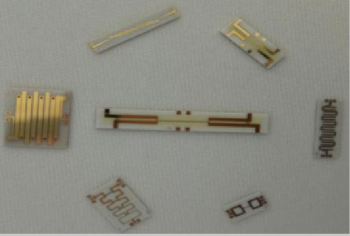 BMBP30R5/4-6PA
BMBP30R5/4-6PA
$49 /Piece
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Ipsam, vero, provident, eum eligendi blanditiis ex explicabo vitae nostrum facilis asperiores dolorem illo officiis ratione vel fugiat dicta laboriosam labore adipisci.
Khaja Road, Bayzid, Chittagong, Bangladesh
Phone: +880-31-000-000
Fax: +880-31-000-000
Email: hello@meghna.com